บทนำ CSS
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) เป็นภาษาที่ใช้สำหรับจัดรูปแบบและออกแบบเว็บเพจ CSS ทำให้เราสามารถควบคุมสี, ขนาด, spacing, positioning และ animation ได้ รวมกับ HTML (โครงสร้าง) และ JavaScript (interactivity) ทำให้เว็บไซต์สมบูรณ์
ความสำคัญของ CSS
CSS เป็นพื้นฐานที่สำคัญในการพัฒนาเว็บ เนื่องจาก:
- แยก Content และ Presentation - HTML เก็บเนื้อหา CSS เก็บรูปแบบ ทำให้โค้ดชัดเจนและง่ายบำรุงรักษา
- Responsive Design - สามารถสร้างเว็บไซต์ที่ทำงานได้บนอุปกรณ์ทุกขนาด
- ประหยัดเวลา - นำ CSS ไปใช้ซ้ำได้หลายครั้งในเอกสาร
- SEO Friendly - เว็บไซต์ที่ออกแบบดีด้วย CSS ได้ ranking ที่ดีในการค้นหา
- Performance - โค้ด CSS ที่ดีช่วยให้เว็บโหลดได้เร็วขึ้น
CSS คืออะไร
CSS ย่อมาจาก "Cascading Style Sheets" และมีบทบาทสำคัญในการออกแบบเว็บ ให้เราลงลึกเข้าไปเรียนรู้รายละเอียด
ความหมาย
CSS ย่อมาจาก Cascading Style Sheets
- Cascading = การไหลแบบชั้น ๆ ซึ่งหมายความว่า rule ต่อมาจะทับบน rule ก่อนหน้าถ้ามี selector เดียวกัน ยิ่งเข้าไปในลึก priority ยิ่งสูง
- Style = รูปแบบ, การจัดรูป ของการแสดงผล
- Sheets = หนังสือ, เอกสาร ที่บรรจุกฎเกณฑ์
Web Design Holy Trinity (สามเหลี่ยมทองของเว็บ)
เว็บไซต์สมบูรณ์ต้องประกอบไปด้วยสามส่วนสำคัญ:
| Technology | บทบาท | ตัวอย่าง |
|---|---|---|
| HTML | โครงสร้าง (Structure) | แท็ก <p>, <div>, <button> |
| CSS | รูปแบบ (Styling) | สี, ขนาด, spacing, layout |
| JavaScript | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ (Interaction) | Click, Hover, Animation events |
CSS ใช้สำหรับอะไร
- ✅ จัดสี (colors) - สีตัวอักษร พื้นหลัง และกรอบ
- ✅ ขนาดตัวอักษร (font sizes) - ขนาด ชนิด น้ำหนัก ของฟอนต์
- ✅ ระยะห่าง (spacing, margins, padding) - ระยะห่างในและนอก element
- ✅ การจัด layout - positioning, flexbox, grid สำหรับจัด element ในหน้า
- ✅ Animation และ transitions - สร้างการเคลื่อนไหว และผลเพิ่มเติม
- ✅ Responsive design - ทำให้เว็บสามารถปรับตัวได้ตามขนาดหน้าจอ
- ✅ Effects - เงา, gradient, filter, transform และอื่นๆ
วิธีใช้ CSS
มีสามวิธีในการเขียน CSS ในเว็บเพจ แต่ละวิธีมีข้อดีและข้อเสีย ลองเรียนรู้ความแตกต่างกัน
1. Inline CSS
เขียน CSS โดยตรงในแท็ก HTML ผ่านทาง style attribute:
<p style="color: red; font-size: 18px;">ข้อความสีแดง</p>
<button style="background-color: blue; color: white; padding: 10px 20px;">
ปุ่มสีน้ำเงิน
</button>- ยากต่อการบำรุงรักษา - ต้องแก้ไขทีละ element
- ไม่สามารถ reuse ได้ - ต้องเขียนซ้ำทุกครั้ง
- ไม่สามารถใช้ advanced features เช่น media queries
- ทำให้ HTML ยุ่มเหยิง ยากต่อการอ่าน
- ต้องการเปลี่ยนรูปแบบเพียงครั้งเดียว
- ทดลอง style ในขั้นพัฒนา
- ใช้เป็นการชั่วคราว
2. Internal CSS
เขียน CSS ในแท็ก <style> ภายใน <head> ของ HTML:
<head>
<style>
/* กำหนด CSS ที่นี่ */
p {
color: red;
font-size: 18px;
line-height: 1.6;
}
button {
background-color: blue;
color: white;
padding: 10px 20px;
}
</style>
</head>- CSS จะอยู่ในเอกสารเดียว
- สามารถจัด selector ได้ดีกว่า Inline
- สามารถใช้ advanced features ได้
- ไม่สามารถแชร์ CSS ระหว่างไฟล์ต่างๆ ได้
- ทำให้ไฟล์ HTML โตขึ้น ซึ่งส่งผลต่อความเร็วในการโหลด
3. External CSS (แนะนำ) ⭐
เขียน CSS ในไฟล์แยกต่างหาก และนำเข้าไปในแท็ก <head>:
<!-- ในไฟล์ HTML -->
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
</head>
<!-- ในไฟล์ style.css -->
p {
color: red;
font-size: 18px;
}
button {
background-color: blue;
color: white;
}- ทำให้ HTML สะอาด และง่ายต่อการอ่าน
- สามารถแชร์ CSS ระหว่างไฟล์ได้ (reusable)
- ปรับปรุง Performance - Browser สามารถแคชไฟล์ CSS ได้
- ง่ายต่อการบำรุงรักษา - แก้ไขในที่เดียว ใช้ทั่วไฟล์
- สามารถจัดระเบียบ code ได้ดี
- หลีกเลี่ยง Selector Conflicts ด้วยการใช้ Namespace หรือ SMACSS
CSS Selectors
Selectors ใช้เพื่อเลือก HTML elements ที่ต้องการจะจัดรูปแบบ มีหลายประเภทให้เลือกตามความเหมาะสม
1. Universal Selector (*)
เลือก ทุก element ในหน้า มักใช้ในการ reset margin และ padding:
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}2. Element Selector
เลือก element โดยใช้ชื่อแท็ก HTML เช่น p, div, h1:
p {
color: blue;
font-size: 16px;
}
h1 {
font-size: 32px;
color: #333;
}3. Class Selector (.)
เลือก element ที่มี class attribute ที่ตรงกัน (สามารถใช้หลายครั้งได้):
.intro {
background-color: yellow;
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.highlight {
background-color: red;
color: white;
}ใช้ในไฟล์ HTML:
<p class="intro">นี่คือ intro</p>
<p class="intro highlight">นี่คือ intro ที่ highlight</p>4. ID Selector (#)
เลือก element ที่มี id attribute ที่ตรงกัน (ควรใช้เพียง ครั้งเดียว ต่อหน้า):
#main-title {
color: red;
text-align: center;
font-size: 40px;
}ใช้ในไฟล์ HTML:
<h1 id="main-title">ชื่อเพจหลัก</h1>5. Attribute Selector ([])
เลือก element ตามค่าของ attribute:
/* เลือก input ที่มี type="text" */
input[type="text"] {
border: 1px solid blue;
padding: 5px;
}
/* เลือก link ที่ target="_blank" */
a[target="_blank"] {
color: green;
text-decoration: underline;
}
/* เลือก input ที่มี disabled attribute */
input[disabled] {
background-color: #ccc;
cursor: not-allowed;
}6. Pseudo-class Selector (:)
เลือก element ในสถานะเฉพาะ เช่น hover, focus, active:
/* เมื่อชี้เม้าส์ที่ link */
a:hover {
color: red;
text-decoration: underline;
}
/* เมื่อปุ่มถูกกด */
button:active {
transform: scale(0.95);
background-color: darkblue;
}
/* เมื่อ input ได้รับ focus (ถูกคลิก) */
input:focus {
outline: 2px solid blue;
border-color: blue;
}
/* สถานะอื่นๆ */
a:visited { color: purple; } /* link ที่เคยคลิกแล้ว */
li:first-child { margin-top: 0; } /* item แรก */
li:last-child { margin-bottom: 0; } /* item สุดท้าย */Selector ที่เฉพาะเจาะจงมากขึ้นจะมี priority สูงกว่า:
- Universal (*) - ต่ำที่สุด
- Element selector (p, div)
- Class selector (.intro)
- ID selector (#main)
- Inline style - สูงที่สุด
CSS Properties
CSS Properties คือคุณสมบัติที่ใช้กำหนดรูปแบบการแสดงผลของ element เช่น สี, ขนาด, ตำแหน่ง ฯลฯ
Syntax
โครงสร้างพื้นฐานของการเขียน CSS:
selector {
property: value;
property: value;
}Commonly Used Properties
- width / height - กำหนดความกว้างและความสูง
- margin / padding - ระยะห่างด้านนอก/ด้านใน
- color - สีตัวอักษร
- background-color - สีพื้นหลัง
- border - กรอบ
- font-size / font-family - ขนาดและชนิดตัวอักษร
- text-align - จัดแนวข้อความ
- display - ลักษณะการแสดงผล
CSS Units
CSS Units เป็นหน่วยวัดที่ใช้ในการกำหนดขนาด, ระยะห่าง และค่าต่าง ๆ ใน CSS ปี ความเข้าใจหน่วยวัดนี้มีความสำคัญต่อการออกแบบ responsive design
ประเภทของ CSS Units
CSS Units แบ่งออกเป็น 3 กลุ่มหลัก:
- Absolute Units - ขนาดคงที่ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง
- Relative Units - ขนาดสัมพันธ์กับค่าอื่น ๆ (flexible)
- Viewport Units - ขนาดสัมพันธ์กับขนาด browser window
1. Absolute Units (หน่วยสัมบูรณ์)
หน่วยที่มีขนาดคงที่ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง ไม่ recommended สำหรับ responsive design:
| Unit | คำอธิบาย | ตัวอย่าง | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| px (pixels) | พิกเซล (หน่วยย่อยของหน้าจอ) | width: 300px; | กำหนดขนาดที่แน่นอน, borders, บางทีเท่านั้น |
| cm (centimeters) | เซนติเมตร (ใช้ยาก) | width: 10cm; | บ่อยครั้งมากจาก media ออกแบบสำหรับการพิมพ์ |
| mm (millimeters) | มิลลิเมตร | width: 100mm; | ใช้สำหรับการพิมพ์ |
| in (inches) | นิ้ว | width: 2in; | ใช้สำหรับการพิมพ์ |
| pt (points) | จุด (1pt = 1/72 นิ้ว) | font-size: 12pt; | สำหรับการพิมพ์ documents |
ไม่ควรใช้ absolute units สำหรับขนาด layout ที่ต้อง responsive เนื่องจาก:
- ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลงตามขนาด browser หรือ device
- ทำให้เว็บไซต์ดูแปลก ๆ บนมือถือ
- ยากต่อการปรับให้เข้ากับอุปกรณ์ต่าง ๆ
ลองใช้ px เฉพาะจำนวนพอเพียง
2. Relative Units (หน่วยสัมพันธ์)
หน่วยที่มีขนาดขึ้นอยู่กับค่าอื่น ๆ อันดับแนนะนำสำหรับ responsive design:
| Unit | Reference | ตัวอย่าง | Responsive |
|---|---|---|---|
| % (percentage) | ขนาดของ parent element | width: 50%; | ✅ ดีมาก |
| em | font-size ของ element นั้น เอง (หรือ parent ถ้าใช้ใน font-size) | width: 2em; (2 เท่าของ font-size) | ✅ ดี |
| rem (root em) | font-size ของ root element (html) | width: 2rem; (2 เท่าของ root font-size) | ✅ ดีมาก (แนะนำ) |
| ch | ความกว้างของตัวอักษร "0" | width: 50ch; (50 ตัวอักษร) | ✅ สำหรับ text |
Percentage (%)
เป็นเปอร์เซ็นต์ของ parent element:
/* HTML */
<div class="container">
<div class="child">Content</div>
</div>
/* CSS */
.container {
width: 800px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #ddd;
}
.child {
width: 50%; /* 50% ของ 800px = 400px */
height: 100%; /* 100% ของ 200px = 200px */
background-color: #0066cc;
}Em Unit
Em = ขนาดสัมพันธ์กับ font-size ของ element นั้นเอง (หรือ parent เมื่อใช้ใน font-size):
/* ตัวอย่าง: em ใน width */
.box {
font-size: 16px;
width: 2em; /* 2 x 16px = 32px */
padding: 1.5em; /* 1.5 x 16px = 24px */
}
/* ตัวอย่าง: em ใน font-size (ดูประวัติ) */
body {
font-size: 16px; /* base size */
}
body p {
font-size: 1em; /* 1 x 16px = 16px (inherit จาก body) */
}
body h1 {
font-size: 2em; /* 2 x 16px = 32px */
}
body h2 {
font-size: 1.5em; /* 1.5 x 16px = 24px */
}
/* ⚠️ ปัญหา: Nesting ใน em */
.outer {
font-size: 20px;
}
.outer .middle {
font-size: 1.5em; /* 1.5 x 20px = 30px */
}
.outer .middle .inner {
font-size: 1.5em; /* 1.5 x 30px = 45px ❌ ใหญ่เกิน! */
}Rem Unit (Root Em) - ⭐ Recommended
Rem = ขนาดสัมพันธ์กับ font-size ของ root element (html) เท่านั้น ง่ายหลายค่านัยมากกว่า em:
/* HTML */
html {
font-size: 16px; /* root size */
}
/* CSS */
body {
font-size: 1rem; /* 1 x 16px = 16px */
}
h1 {
font-size: 2rem; /* 2 x 16px = 32px */
}
h2 {
font-size: 1.5rem; /* 1.5 x 16px = 24px */
}
p {
font-size: 1rem;
margin-bottom: 1rem;
padding: 0.5rem;
}
.btn {
font-size: 0.875rem; /* 0.875 x 16px = 14px */
padding: 0.5rem 1rem;
margin: 1rem 0;
}
/* ✅ ข้อดี Rem:
* - Consistent ตลอดทั้ง document
* - ไม่มีปัญหา nesting เหมือน em
* - ง่ายต่อการปรับ global font-size
*/Practical Example: Em vs Rem
/* Em Example - ปัญหา Nesting */
.card {
font-size: 16px;
}
.card-title {
font-size: 1.5em; /* 16 x 1.5 = 24px ✅ */
}
.card .nested {
font-size: 1.5em; /* 24 x 1.5 = 36px ❌ ใหญ่เกิน! */
}
/* Rem Example - Consistent */
html {
font-size: 16px;
}
.card {
font-size: 1rem; /* 16px */
}
.card-title {
font-size: 1.5rem; /* 24px ✅ */
}
.card .nested {
font-size: 1.5rem; /* 24px ✅ สอดคล้องกับข้างบน */
}3. Viewport Units (หน่วยมุมมอง)
ขนาดสัมพันธ์กับขนาด browser window (viewport):
| Unit | คำอธิบาย | ตัวอย่าง | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| vw (viewport width) | 1% ของความกว้าง browser | width: 50vw; (ครึ่งหนึ่งของ window) | Full-width sections, responsive fonts |
| vh (viewport height) | 1% ของความสูง browser | height: 100vh; (เต็มหน้าจอ) | Hero sections, full-page layouts |
| vmin | 1% ของค่าที่เล็กกว่า (width หรือ height) | font-size: 5vmin; | Responsive font ที่สมดุล |
| vmax | 1% ของค่าที่ใหญ่กว่า (width หรือ height) | font-size: 5vmax; | ใช้น้อย |
/* Full-screen Hero Section */
.hero {
height: 100vh; /* เต็มหน้าจอ */
width: 100vw; /* เต็มความกว้าง */
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
background: linear-gradient(to right, #667eea 0%, #764ba2 100%);
}
.hero h1 {
font-size: 8vw; /* ขยาย/หดฟอนต์ตามความกว้าง */
color: white;
}
/* Responsive Font ที่สมดุล */
.heading {
font-size: 5vmin; /* ใช้ค่าที่เล็กกว่าเพื่อให้ดูสมดุล */
}
/* Section กว้างครึ่งหนึ่ง */
.sidebar {
width: 50vw;
height: 100vh;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
}Comparison Table: เลือกหน่วยไหนดี
| Unit | ขึ้นอยู่กับ | Flexible | แนะนำใช้ |
|---|---|---|---|
| px | Fixed size | ❌ No | Borders, shadows, specific details |
| % | Parent size | ✅ Yes | Width, padding, layout spacing |
| em | Current font-size | ✅ Yes (but complex) | Relative sizing (use carefully) |
| rem | Root font-size | ✅ Yes | ⭐ Font sizes, margins, padding |
| vw/vh | Viewport | ✅ Yes (very) | Full-screen sections, responsive fonts |
Best Practices
- ใช้ rem สำหรับ typography - ขนาดตัวอักษร, margins, padding ที่เข้าสัดส่วน
- ใช้ % สำหรับ layout widths - ความกว้างของ containers ที่ต้อง responsive
- ใช้ em สำหรับส่วนที่เกี่ยวข้องกับ font - border-radius, letter-spacing ที่เกี่ยวกับขนาดฟอนต์
- ใช้ vw/vh สำหรับ full-screen sections - Hero sections, full-page layouts
- หลีกเลี่ยง px ในปริมาณมาก - ทำให้เว็บไม่ responsive
- กำหนด base font-size ใน html - เพื่อให้ rem ทำงานอย่างถูกต้อง
Complete Example: Units in Action
/* Setup */
html {
font-size: 16px; /* base: 1rem = 16px */
}
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
/* Layout */
body {
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, 'Segoe UI', Roboto, sans-serif;
font-size: 1rem; /* 16px */
line-height: 1.6;
color: #333;
}
.container {
max-width: 1200px; /* px for max constraint */
width: 90%; /* % for responsiveness */
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 2rem; /* rem for spacing */
}
/* Typography */
h1 {
font-size: 2.5rem; /* 40px */
margin-bottom: 1.5rem; /* 24px */
line-height: 1.2;
}
h2 {
font-size: 2rem; /* 32px */
margin-bottom: 1rem; /* 16px */
margin-top: 2rem;
}
p {
font-size: 1rem; /* 16px */
margin-bottom: 1.5rem;
line-height: 1.6;
}
/* Components */
.btn {
display: inline-block;
padding: 0.75rem 1.5rem; /* rem for scalability */
font-size: 1rem;
border-radius: 0.25rem; /* em-like: scaled with font */
border: 1px solid #ccc; /* px for thin line */
cursor: pointer;
}
.card {
padding: 2rem;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 0.5rem;
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
/* Responsive */
@media (max-width: 768px) {
html {
font-size: 14px; /* smaller base on mobile */
}
.container {
width: 95%;
padding: 1rem;
}
h1 {
font-size: 1.75rem;
}
}Color & Text
Color และ Text properties เป็นอย่างหนึ่งที่ใช้บ่อยที่สุดในการจัดรูปแบบเนื้อหา เนื่องจากส่วนใหญ่เว็บไซต์เต็มไปด้วยตัวอักษร
Color Formats
มี 4 วิธีหลักในการกำหนดสี ในภาษา CSS:
/* 1. Named colors - ชื่อสีที่ Browser รู้จัก */
color: red;
color: blue;
color: lightblue;
/* 2. HEX colors - รหัสสีในระบบเลขฐาน 16 (#RRGGBB) */
color: #ff0000; /* สีแดง */
color: #00ff00; /* สีเขียว */
color: #0000ff; /* สีน้ำเงิน */
/* 3. RGB colors - ค่า Red Green Blue (0-255) */
color: rgb(255, 0, 0); /* สีแดง */
color: rgb(0, 255, 0); /* สีเขียว */
color: rgb(0, 0, 255); /* สีน้ำเงิน */
/* 4. RGBA colors - RGB + Alpha (transparency) 0-1 */
color: rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.5); /* สีแดง โปร่งใสครึ่ง */
color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.8); /* สีดำ โปร่งใส 80% */- Named colors - ใช้สำหรับสีพื้นฐาน เช่น red, blue, black
- HEX colors - ใช้บ่อยที่สุด ในการออกแบบ (เข้าใจง่าย)
- RGB colors - ใช้เมื่อต้องการคำนวณสี dynamically
- RGBA colors - ใช้เมื่อต้องการความเป็นโปร่งใส (transparency)
Font Properties
จัดรูปแบบตัวอักษรเพื่อให้อ่านง่ายและสวยงาม:
/* Font family - เลือกชนิดตัวอักษร */
font-family: Arial, sans-serif; /* หลัก, fallback */
font-family: 'Courier New', monospace; /* สำหรับ code */
/* Font size - ขนาดตัวอักษร */
font-size: 16px; /* ค่าเริ่มต้น */
font-size: 1.2em; /* relative กับ parent */
font-size: 1rem; /* relative กับ root (16px) */
/* Font weight - น้ำหนัก (100-900) */
font-weight: normal; /* 400 */
font-weight: bold; /* 700 */
font-weight: 600; /* semi-bold */
/* Font style - ลักษณะ */
font-style: normal; /* ปกติ */
font-style: italic; /* เอียง */
font-style: oblique; /* เอียงมากกว่า italic */
/* Line height - ระยะห่างบรรทัด (readability) */
line-height: 1.5; /* 1.5 เท่าของ font-size */
line-height: 1.6; /* แนะนำสำหรับ body text */
/* Text align - จัดแนวข้อความ */
text-align: left; /* ชิดซ้าย (ค่าเริ่มต้น) */
text-align: center; /* กลาง */
text-align: right; /* ชิดขวา */
text-align: justify; /* เต็มแนว */
/* Text decoration - ตกแต่งข้อความ */
text-decoration: none; /* ไม่มี */
text-decoration: underline; /* ขีดใต้ */
text-decoration: overline; /* ขีดบน */
text-decoration: line-through; /* ขีดกลาง */
/* Text transform - ตัวพิมพ์ */
text-transform: uppercase; /* ตัวใหญ่ทั้งหมด */
text-transform: lowercase; /* ตัวเล็กทั้งหมด */
text-transform: capitalize; /* ตัวแรกใหญ่ */
/* Letter spacing - ระยะห่างตัวอักษร */
letter-spacing: 0.1em; /* เพิ่มระยะห่าง */
/* Word spacing - ระยะห่างคำ */
word-spacing: 0.2em;Complete Font Example
/* Shorthand - รวมทั้งหมด */
font: italic 600 18px/1.6 'Segoe UI', sans-serif;
/* style weight size/height family fallback */
/* Body text - การอ่านที่สะดวก */
body {
font-family: 'Segoe UI', Tahoma, Geneva, Verdana, sans-serif;
font-size: 16px; /* ขนาดอ่านง่าย */
font-weight: 400; /* regular weight */
line-height: 1.6; /* ระยะห่างบรรทัดดี */
color: #333; /* สีเข้มเพื่อให้อ่านง่าย */
}
/* Heading - ชัดเจน ดึงดูดสายตา */
h1 {
font-size: 2.5em;
font-weight: 700;
line-height: 1.2;
color: #000;
}Box Model
Box Model คือแนวคิดหลักที่อธิบายว่า Browser แสดงผล HTML elements ทุกตัวถูก visualize เป็น box ที่ประกอบไปด้วย 4 ชั้น
Structure of Box Model
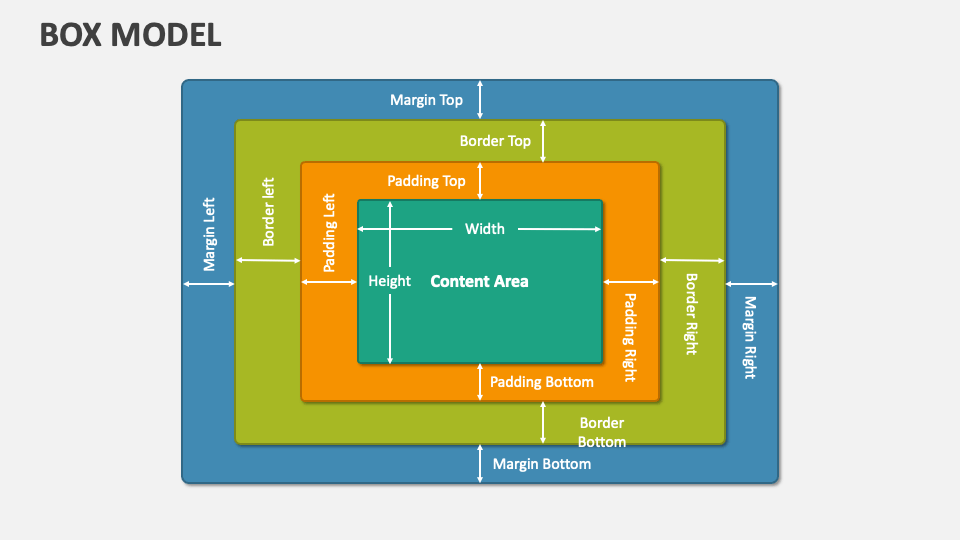
Content
ส่วนที่มีข้อมูลจริง (ตัวอักษร, รูปภาพ, ฯลฯ) กำหนดด้วย width และ height
Padding (ระยะห่างด้านใน)
ระยะห่างระหว่าง content และ border มักใช้เพื่อให้มีอากาศ ภายใน element:
/* 4 ด้าน */
padding: 20px; /* ทั้งสี่ด้าน 20px */
/* 2 ค่า */
padding: 10px 20px; /* บน/ล่าง 10px, ซ้าย/ขวา 20px */
padding: 10px 20px 15px 25px; /* บน ขวา ล่าง ซ้าย (ตามเข็มนาฬิกา) */
/* ด้านเดียว */
padding-top: 10px;
padding-right: 15px;
padding-bottom: 10px;
padding-left: 15px;Border (กรอบ)
กรอบรอบ element ตั้งอยู่ระหว่าง padding และ margin:
/* Basic border */
border: 1px solid black; /* width style color */
border: 2px dashed red; /* dashed border */
border: 3px dotted blue; /* dotted border */
/* Border style options */
border-style: solid; /* เส้นทึบ */
border-style: dashed; /* เส้นประ */
border-style: dotted; /* จุด */
border-style: double; /* เส้นคู่ */
border-style: none; /* ไม่มี */
/* Border radius - มุมโค้ง */
border-radius: 5px; /* มุมโค้ง 5px ทั้ง 4 มุม */
border-radius: 50%; /* วงกลม (กว้าง/สูง = 50%) */
border-radius: 5px 10px; /* มุมบน-ล่าง-ซ้าย 5px, มุมบน-ล่าง-ขวา 10px */
/* ด้านเดียว */
border-top: 1px solid black;
border-right: 2px solid blue;
border-bottom: 1px solid red;
border-left: 3px solid green;Margin (ระยะห่างด้านนอก)
ระยะห่างนอก element ใช้เพื่อสร้างอากาศระหว่าง elements:
/* 4 ด้าน */
margin: 20px; /* ทั้งสี่ด้าน 20px */
/* 2 ค่า */
margin: 10px 20px; /* บน/ล่าง 10px, ซ้าย/ขวา 20px */
/* 4 ค่า */
margin: 10px 15px 20px 25px; /* บน ขวา ล่าง ซ้าย */
/* Center horizontally */
margin: 0 auto; /* ศูนย์บนล่าง, auto ซ้ายขวา = center */
/* ด้านเดียว */
margin-top: 20px;
margin-right: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
margin-left: 15px;Box Sizing
กำหนดว่า width และ height ใน style นั้นรวม padding/border หรือไม่:
/* content-box (default) - width = content only */
box-sizing: content-box;
/* border-box - width = content + padding + border (แนะนำ) */
box-sizing: border-box;
/* ใช้ border-box ทั่วไป */
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}Box Model Example
.card {
width: 300px;
padding: 20px; /* ระยะห่างใน */
border: 2px solid #ddd; /* กรอบ */
border-radius: 8px; /* มุมโค้ง */
margin: 20px; /* ระยะห่างนอก */
box-sizing: border-box; /* รวม padding ในความกว้าง */
}
/* ผลลัพธ์: */
/* Total width = 300px (width + padding + border แล้ว) */Positioning
Position ใช้สำหรับควบคุมตำแหน่งของ element บนหน้าเว็บ มี 5 แบบที่สำคัญ: static, relative, absolute, fixed, และ sticky เลือกแบบที่เหมาะสมกับการออกแบบของคุณ
1. Static (ค่าเริ่มต้น)
Static เป็นค่าเริ่มต้นของ position ทุก element จะอยู่ในตำแหน่งตามปกติใน document flow (ไม่ขึ้นไป ลงมา ไป ซ้าย ขวา) ไม่สามารถใช้ top, bottom, left, right ได้:
/* Static position - ค่าเริ่มต้น */
.element {
position: static;
/* top, bottom, left, right ใช้ไม่ได้ */
}
/* ผลลัพธ์: element อยู่ที่เดิม */
/* ไม่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงตำแหน่ง */2. Relative (สัมพัธ์กับตำแหน่งเดิม)
Relative ย้ายตำแหน่งเทียบกับตำแหน่งเดิมของ element แต่ยังคงใช้พื้นที่ของตำแหน่งเดิม (ไม่กระทบ element อื่น):
/* Relative position - ย้ายจากตำแหน่งเดิม */
.element {
position: relative;
top: 20px; /* ย้ายลง 20px */
left: 30px; /* ย้ายไป 30px */
}
/* ผลลัพธ์: */
/* - Element ย้ายตำแหน่ง */
/* - ยังคงใช้พื้นที่เดิม (ไม่กระทบ element อื่น) */
/* - เหมาะสำหรับปรับแต่งตำแหน่งเล็กน้อย */
/* ตัวอย่างจริง: ปรับตำแหน่ง text ไปด้านบน-ขวา */
.label {
position: relative;
top: -5px; /* ขึ้น 5px */
left: 10px; /* ไป 10px */
}3. Absolute (สัมพัธ์กับ parent ที่มี position)
Absolute นำ element ออกจาก normal document flow และวางตำแหน่งเทียบกับ parent ที่มี position ที่ไม่ใช่ static (ถ้าไม่มี จะเทียบกับ viewport):
/* Parent container ต้องมี position (ไม่ใช่ static) */
.container {
position: relative; /* ต้องกำหนด */
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
/* Child element ใช้ absolute */
.child {
position: absolute;
top: 10px; /* ห่างจากด้านบนของ parent 10px */
left: 20px; /* ห่างจากด้านซ้ายของ parent 20px */
width: 100px;
}
/* ผลลัพธ์: */
/* - Element ออกจาก document flow */
/* - วางตำแหน่งเทียบกับ parent (container) */
/* - ไม่ใช้พื้นที่ของ parent (stacking order) */
/* ตัวอย่าง: Badge ที่มุมบนขวา */
.card {
position: relative;
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
}
.badge {
position: absolute;
top: -5px;
right: -5px;
background: red;
color: white;
padding: 5px 10px;
border-radius: 50%;
}4. Fixed (สัมพัธ์กับ viewport)
Fixed วางตำแหน่งเทียบกับ viewport (หน้าจออุปกรณ์) ไม่เลื่อนไปกับการ scroll content:
/* Fixed position - ติดกับหน้าจอ */
.navbar {
position: fixed;
top: 0; /* ติดด้านบน */
left: 0; /* ติดด้านซ้าย */
right: 0; /* ติดด้านขวา */
width: 100%;
background: white;
box-shadow: 0 2px 5px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
z-index: 1000; /* ต้องกำหนด z-index เพื่อให้อยู่บนสุด */
}
/* ป้องกันไม่ให้ navbar ทับ content */
body {
margin-top: 60px; /* ให้พื้นที่สำหรับ navbar */
}
/* ตัวอย่าง: Fixed sidebar */
.sidebar {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 250px;
height: 100vh; /* ความสูงเต็มหน้าจอ */
background: #f0f0f0;
overflow-y: auto;
}
/* ตัวอย่าง: Back to top button */
.back-to-top {
position: fixed;
bottom: 20px;
right: 20px;
background: #3498db;
color: white;
padding: 10px 15px;
border-radius: 50%;
cursor: pointer;
}5. Sticky (สัมพัธ์กับ scroll container)
Sticky รวมพฤติกรรมของ relative และ fixed - ปกติเป็น relative แต่เมื่อ scroll ถึงตำแหน่งที่กำหนดจะติดเหมือน fixed:
/* Sticky position - ติดเมื่อ scroll ถึง */
.header {
position: sticky;
top: 0; /* ติดด้านบนเมื่อ scroll ถึง top: 0 */
background: white;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
z-index: 100; /* ให้อยู่บนสุด */
}
/* ผลลัพธ์: */
/* - ปกติ: header อยู่ตามตำแหน่ง normal */
/* - scroll ไป: header ติดด้านบนของ viewport */
/* - ออกจาก container: header หายไปพร้อม container */
/* ตัวอย่าง: Sticky table header */
table {
width: 100%;
}
thead {
position: sticky;
top: 0;
background: #f0f0f0;
}
th {
padding: 10px;
}
/* ตัวอย่าง: Sticky sidebar ใน 2 column layout */
.sidebar {
position: sticky;
top: 20px; /* ห่างจากด้านบน 20px */
height: fit-content;
}
.content {
flex: 1;
}📋 Position Values Comparison
| Position | ความหมาย | อ้างอิงกับ | ใช้เมื่อ | ตัวอย่าง |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| static | ค่าเริ่มต้น | Document flow | ไม่ต้องย้ายตำแหน่ง | ข้อความปกติ |
| relative | ย้ายจากตำแหน่งเดิม | ตำแหน่ง static เดิม | ปรับแต่งตำแหน่งเล็กน้อย | ย้ายข้อความขึ้น 5px |
| absolute | ออกจาก flow | Parent ที่มี position | วางตำแหน่งอิสระ | Badge, tooltip, dropdown |
| fixed | ติดกับหน้าจอ | Viewport | ติดที่หน้าจอ | Navbar, floating button |
| sticky | Hybrid (relative + fixed) | Parent + Viewport | ติดเมื่อ scroll ถึง | Table header, section title |
🔑 Key Properties for Positioning
/* ใช้กับ relative, absolute, fixed, sticky */
/* Top, Bottom, Left, Right */
.element {
position: absolute;
top: 10px; /* ห่างจากด้านบน */
bottom: 10px; /* ห่างจากด้านล่าง */
left: 20px; /* ห่างจากด้านซ้าย */
right: 20px; /* ห่างจากด้านขวา */
}
/* Z-index - ควบคุมลำดับการ stack */
.overlay {
position: absolute;
z-index: 10; /* ยิ่งสูง ยิ่งอยู่บนสุด */
}
/* ตัวอย่าง: Center element ที่ absolute */
.centered {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
width: 300px;
}❌ Common Positioning Mistakes
/* ❌ ไม่ดี - parent ไม่มี position */
.container {
width: 300px;
/* ไม่มี position: relative; */
}
.child {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
/* จะอ้างอิงกับ viewport ไม่ใช่ container */
}
/* ✅ ดี - parent มี position */
.container {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
}
.child {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
/* อ้างอิงกับ container อย่างถูกต้อง */
}/* ❌ ไม่ดี - fixed navbar ทับเนื้อหา */
.navbar {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
}
body {
/* ไม่มี padding/margin */
margin-top: 0;
}
/* ✅ ดี - เพิ่มพื้นที่สำหรับ navbar */
.navbar {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 60px;
}
body {
margin-top: 60px; /* ให้พื้นที่ */
}/* ❌ ไม่ดี - overflow:hidden ใน parent */
.container {
overflow: hidden;
/* sticky จะไม่ทำงาน */
}
.header {
position: sticky;
top: 0;
}
/* ✅ ดี - ไม่มี overflow */
.container {
/* ไม่มี overflow */
}
.header {
position: sticky;
top: 0;
}Display & Layout
Display property กำหนดว่า element จะแสดงผลในลักษณะใด ซึ่งส่งผลต่อการจัด layout ของเพจ
Display Values
/* Block: ยาวเต็มแนว ขึ้นบรรทัดใหม่ */
display: block;
/* Inline: ในแนวเดียวกัน ไม่ขึ้นบรรทัด */
display: inline;
/* Inline-block: เหมือน inline แต่สามารถกำหนด width/height */
display: inline-block;
/* None: ซ่อนไปไม่แสดงผล */
display: none;
/* Flex: ใช้ Flexbox layout */
display: flex;
/* Grid: ใช้ Grid layout */
display: grid;Block vs Inline vs Inline-block
| Property | Width/Height | ขึ้นบรรทัดใหม่ | ตัวอย่าง |
|---|---|---|---|
| block | ✅ ได้ | ✅ ใช่ | <div>, <p>, <h1> |
| inline | ❌ ไม่ได้ | ❌ ไม่ | <span>, <a>, <strong> |
| inline-block | ✅ ได้ | ❌ ไม่ | <button>, <img> |
Flexbox
Flexbox (Flexible Box Layout) เป็นวิธีจัด layout ที่ยืดหยุ่นและมีประสิทธิภาพ เหมาะสำหรับการจัด element ในแนวเดียว (1 มิติ)
Container Properties
คุณสมบัติที่กำหนดให้กับ container เพื่อควบคุมการจัด items:
.container {
display: flex;
/* direction */
flex-direction: row; /* ซ้ายไปขวา (ค่าเริ่มต้น) */
/* column: บนลงล่าง */
/* wrap */
flex-wrap: wrap; /* ขึ้นบรรทัดใหม่เมื่อไม่พอ */
/* content alignment */
justify-content: space-between; /* flex-start, flex-end, center */
/* item alignment */
align-items: center; /* flex-start, flex-end, stretch */
/* ระยะห่าง */
gap: 20px;
}Item Properties
คุณสมบัติที่กำหนดให้กับแต่ละ item ภายใน container:
.item {
flex: 1; /* grow shrink basis */
flex-grow: 1; /* เพิ่มพื้นที่ว่าง */
align-self: center; /* override align-items */
}- จัด items ในแนวเดียว (แนวนอน/แนวตั้ง)
- ต้องการ responsive layout ที่ง่าย
- จัด navigation, buttons, card layouts
CSS Grid
CSS Grid เป็นระบบจัด layout ที่มีประสิทธิภาพสำหรับการจัด element แบบ 2 มิติ (แถว + คอลัมน์) เหมาะสำหรับการสร้าง layout ที่ซับซ้อน
Container Properties
กำหนดให้กับ grid container เพื่อสร้างโครงสร้าง grid:
.container {
display: grid;
/* กำหนด columns */
grid-template-columns: 200px 1fr 200px; /* 3 columns */
grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr); /* 3 equal columns */
grid-template-columns: repeat(auto-fit, minmax(200px, 1fr)); /* responsive */
/* กำหนด rows */
grid-template-rows: 100px 1fr 50px;
grid-auto-rows: 100px; /* auto create rows */
/* ระยะห่าง */
gap: 20px;
}Item Properties
ควบคุมตำแหน่งและขนาดของแต่ละ item:
.item {
grid-column: 1 / 3; /* from column 1 to 3 */
grid-row: 1 / 3; /* from row 1 to 3 */
justify-self: center; /* horizontal alignment */
align-self: center; /* vertical alignment */
}- จัด layout ที่ซับซ้อน (2 มิติ)
- สร้าง page layout ทั้งหน้า
- ต้องการควบคุมทั้งแถวและคอลัมน์พร้อมกัน
- สร้าง dashboard, gallery, templates
Responsive Design
Responsive Design คือการออกแบบเว็บไซต์ให้ทำงานได้ดีบนอุปกรณ์ทุกขนาด (smartphone, tablet, desktop) โดยปรับปรุงขนาดและการจัด layout โดยอัตโนมัติ ถือเป็นสิ่งสำคัญในยุคปัจจุบัน เนื่องจากผู้ใช้ส่วนใหญ่เข้าเว็บจากมือถือ
Why Responsive Design Matters
- Mobile-First World - ผู้ใช้ส่วนใหญ่ (60-70%) เข้าจากมือถือ
- SEO Ranking - Google ให้ ranking ที่ดีกว่า responsive sites
- Better UX - ผู้ใช้ได้ประสบการณ์ที่เหมาะสมบนอุปกรณ์ของตัวเอง
- Cost Effective - เว็บเดียว ใช้ได้ทุกอุปกรณ์ (ไม่ต้องสร้าง app แยก)
- Future Proof - อุปกรณ์ใหม่ๆ ออกมาเรื่อย responsive design ทำให้รองรับได้เอง
Mobile-First Approach
วิธีการออกแบบที่แนะนำ - เขียน CSS สำหรับมือถือก่อน แล้วค่อยเพิ่มเติมสำหรับหน้าจอใหญ่:
เขียน CSS สำหรับมือถือก่อนแล้วเพิ่มเติมสำหรับหน้าจออื่น:
/* Base: Mobile */
.container {
width: 100%;
font-size: 14px;
}
/* Tablet */
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.container {
width: 750px;
font-size: 16px;
}
}
/* Desktop */
@media (min-width: 1024px) {
.container {
width: 960px;
font-size: 18px;
}
}
/* Large Desktop */
@media (min-width: 1200px) {
.container {
width: 1140px;
}
}Common Breakpoints
| Device | Screen Width | Media Query |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile (Small) | 320px - 479px | @media (max-width: 479px) |
| Mobile (Large) | 480px - 767px | @media (min-width: 480px) |
| Tablet | 768px - 1023px | @media (min-width: 768px) |
| Desktop | 1024px - 1199px | @media (min-width: 1024px) |
| Large Desktop | 1200px+ | @media (min-width: 1200px) |
Responsive Techniques
1. Flexible Widths & Fluid Layouts
ใช้ width แบบ relative (%, em, rem) แทน pixel คงที่ เพื่อให้ content ปรับตัวตามหน้าจอ:
/* ❌ ไม่ดี - ขนาดคงที่ */
.container {
width: 1200px; /* จะเกินหน้าจอ mobile */
margin: 0 auto;
}
/* ✅ ดี - ปรับตัวได้ */
.container {
width: 90%; /* ปรับตามหน้าจอ */
max-width: 1200px; /* ไม่ใหญ่เกินไป */
margin: 0 auto;
}2. Flexible Images
ทำให้รูปภาพปรับตัวตามขนาด container โดยไม่เกินขนาดเดิม:
/* ทำให้รูปขยายหรือหดตามขนาด container */
img {
max-width: 100%;
height: auto; /* รักษา aspect ratio */
display: block; /* ลบ inline space */
}
/* ตัวอย่างอื่น - background image */
.hero {
background-image: url('hero.jpg');
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
}3. Flexbox & Grid for Layout
ใช้ Flexbox เพื่อสร้าง layout ที่ปรับตัวได้ตามพื้นที่:
/* Flexbox - ปรับตัวตามขนาด */
.grid {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
gap: 20px;
}
.grid-item {
flex: 1 1 250px; /* min 250px, grow if space */
min-width: 0; /* ให้ content ปรับตัว */
}
/* Mobile: column */
@media (max-width: 768px) {
.grid {
flex-direction: column;
}
}4. Media Queries
เปลี่ยน CSS ตามขนาดหน้าจอโดยใช้ @media:
/* Mobile First - เขียน base styles สำหรับ mobile */
.card {
font-size: 14px;
padding: 10px;
}
/* Tablet */
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.card {
font-size: 16px;
padding: 20px;
columns: 2;
}
}
/* Desktop */
@media (min-width: 1024px) {
.card {
font-size: 18px;
columns: 3;
}
}5. Responsive CSS Units
/* Relative units ปรับตามขนาดหน้าจอ */
.container {
width: 90%; /* เปอร์เซ็นต์ของ parent */
padding: 1rem; /* สัมพัธ์กับ root font-size (16px) */
margin: 1em; /* สัมพัธ์กับ element font-size */
height: 100vh; /* 100% ของ viewport height */
}
/* ใช้เมื่อไร */
/* px: ขนาดแน่นอน (border, icon) */
/* %: width/height สัมพัธ์กับ parent */
/* em: padding/margin/font ที่เปลี่ยนตามองค์ประกอบ */
/* rem: padding/margin/font ที่สม่ำเสมอทั่วไซต์ */
/* vh/vw: หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ (hero section, full screen) */Viewport Meta Tag (Required!)
สำคัญมาก! ต้องเพิ่ม meta tag นี้ในไฟล์ HTML head เพื่อให้ responsive design ทำงานบน mobile device:
<!-- ในไฟล์ HTML head section -->
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
/* attribute หมายความว่า: */
/* width=device-width: ใช้ความกว้างจริงของอุปกรณ์ */
/* initial-scale=1.0: ขยาย 100% เมื่อเปิดหน้า */Transitions & Animations
Transitions และ Animations ใช้สำหรับสร้างการเปลี่ยนแปลงและการเคลื่อนไหว ทำให้เว็บไซต์ดูมีชีวิติและประสบการณ์ผู้ใช้ดีขึ้น ความแตกต่างคือ Transition ตอบสนองต่อ event ส่วน Animation ทำงานอัตโนมัติตามแบบที่กำหนด
Transitions - Smooth Property Changes
Transition ใช้เมื่อต้องการให้ property เปลี่ยนแปลงไป ค่อยๆ เนื้อที่ (animation) เมื่อเกิด event เช่น hover, focus, click:
Basic Transition Syntax
/* ตัวอักษร: property duration timing-function delay */
transition: background-color 0.3s ease 0s;
/* Shorthand */
transition: 0.3s ease; /* ใช้กับ ALL properties ที่เปลี่ยน */
/* Multiple properties */
transition: background-color 0.3s ease,
transform 0.3s ease,
box-shadow 0.3s ease;Transition Properties Explained
| Property | ความหมาย | ตัวอย่าง |
|---|---|---|
| transition-property | Property ที่จะเปลี่ยน (ALL, color, etc.) | transition-property: background-color; |
| transition-duration | ระยะเวลา (milliseconds หรือ seconds) | transition-duration: 0.3s; /* 300ms */ |
| transition-timing-function | ลักษณะการเปลี่ยน (ease, linear, ease-in, ease-out, ease-in-out, cubic-bezier) | transition-timing-function: ease-in-out; |
| transition-delay | ความล่าช้าก่อนเริ่ม (milliseconds หรือ seconds) | transition-delay: 0.1s; |
Practical Transition Examples
/* Example 1: Button hover effect */
.button {
background-color: #3498db;
color: white;
padding: 10px 20px;
border: none;
cursor: pointer;
/* ทำให้ color เปลี่ยนแบบ smooth */
transition: background-color 0.3s ease;
}
.button:hover {
background-color: #2980b9;
}
/* Example 2: Card with multiple transitions */
.card {
background-color: white;
transform: scale(1);
box-shadow: 0 2px 5px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
padding: 20px;
/* ทำให้หลาย property เปลี่ยนพร้อมกัน */
transition: background-color 0.3s ease,
transform 0.3s ease,
box-shadow 0.3s ease;
}
.card:hover {
background-color: #f0f0f0;
transform: scale(1.05); /* ขยาย 5% */
box-shadow: 0 5px 15px rgba(0,0,0,0.3);
}
/* Example 3: Different timing functions */
.box-linear {
transition: all 1s linear;
}
.box-ease-in {
transition: all 1s ease-in; /* ช้าแล้วเร็วขึ้น */
}
.box-ease-out {
transition: all 1s ease-out; /* เร็วแล้วช้าลง */
}
.box-ease-in-out {
transition: all 1s ease-in-out; /* ช้า-เร็ว-ช้า */
}Animations - Keyframe-based Motion
Animation ใช้สำหรับการเคลื่อนไหวที่ซับซ้อนมากขึ้น โดยกำหนด keyframes ที่อธิบายต่างๆ ของการเคลื่อนไหว:
Keyframes Syntax
/* ขั้นตอนการเคลื่อนไหว */
@keyframes slide {
0% { /* ตำแหน่งเริ่มต้น */
left: 0;
opacity: 0;
}
50% { /* ตำแหน่งกลาง */
opacity: 1;
}
100% { /* ตำแหน่งสุดท้าย */
left: 200px;
opacity: 1;
}
}
/* ใช้ animation */
.box {
animation: slide 2s linear infinite;
/* ชื่อ ระยะเวลา timing-function นำซ้ำ */
}Animation Properties
| Property | ความหมาย | ตัวอย่าง |
|---|---|---|
| animation-name | ชื่อ @keyframes ที่จะใช้ | animation-name: slide; |
| animation-duration | นาทีที่การเคลื่อนไหวใช้เวลา | animation-duration: 2s; |
| animation-timing-function | ลักษณะการเคลื่อนไหว | animation-timing-function: ease; |
| animation-iteration-count | กี่ครั้ง (ตัวเลข หรือ infinite) | animation-iteration-count: infinite; |
| animation-delay | ความล่าช้าก่อนเริ่ม | animation-delay: 0.5s; |
| animation-direction | ทิศทาง (normal, reverse, alternate, alternate-reverse) | animation-direction: alternate; |
Practical Animation Examples
/* Example 1: Pulse effect */
@keyframes pulse {
0%, 100% {
transform: scale(1);
opacity: 1;
}
50% {
transform: scale(1.1);
opacity: 0.8;
}
}
.pulse {
animation: pulse 1s ease-in-out infinite;
}
/* Example 2: Rotate animation */
@keyframes rotate {
from {
transform: rotate(0deg);
}
to {
transform: rotate(360deg);
}
}
.spinner {
animation: rotate 2s linear infinite;
}
/* Example 3: Bounce animation */
@keyframes bounce {
0%, 100% {
transform: translateY(0);
}
50% {
transform: translateY(-20px);
}
}
.bouncing-ball {
animation: bounce 0.6s ease-in-out infinite;
}
/* Example 4: Slide-in animation */
@keyframes slideInLeft {
from {
opacity: 0;
transform: translateX(-100px);
}
to {
opacity: 1;
transform: translateX(0);
}
}
.card {
animation: slideInLeft 0.5s ease-out;
}Transforms - Shape & Position Changes
Transform ใช้เพื่อเปลี่ยนแปลงรูปร่าง, ตำแหน่ง, มุมและขนาดของ element (อันไม่กระทบ layout อื่น) มักจะใช้ร่วมกับ Transitions หรือ Animations:
2D Transform Functions
/* Rotate - หมุน (0-360 องศา) */
transform: rotate(45deg);
/* Scale - ขยาย/หด (1 = ปกติ, 2 = ใหญ่เป็น 2 เท่า) */
transform: scale(1.5); /* ขยายทั้งแกน X และ Y */
transform: scaleX(0.5); /* หด ตามแนว X */
transform: scaleY(0.5); /* หด ตามแนว Y */
/* Translate - เลื่อน (px หรือ %) */
transform: translate(20px, -10px); /* เลื่อน X 20px, Y -10px */
transform: translateX(20px); /* เลื่อนตามแนว X */
transform: translateY(-10px); /* เลื่อนตามแนว Y */
/* Skew - เบนเสียว */
transform: skew(10deg, 20deg);
/* Combine multiple transforms */
transform: rotate(45deg) scale(1.5) translate(10px, 20px);3D Transform Functions
/* 3D Rotate - หมุนในพื้นที่ 3D */
transform: rotateX(45deg); /* หมุนรอบแกน X */
transform: rotateY(45deg); /* หมุนรอบแกน Y */
transform: rotateZ(45deg); /* หมุนรอบแกน Z (เหมือน 2D rotate) */
/* 3D Translate */
transform: translateZ(50px); /* เลื่อนออกจากหน้าจอ */
transform: translate3d(10px, 20px, 50px);
/* 3D Perspective (เพื่อให้เห็นความลึก) */
.container {
perspective: 1000px;
}
.box {
transform: rotateY(45deg);
}Transform with Transitions Example
/* ผสม Transform กับ Transition เพื่อสร้าง smooth effect */
.card {
transform: scale(1) rotateY(0deg);
transition: transform 0.3s ease;
}
.card:hover {
transform: scale(1.1) rotateY(5deg);
}💡 Transitions vs Animations Comparison
| ลักษณะ | Transition | Animation |
|---|---|---|
| ใช้ได้เมื่อ | ตอบสนองต่อ event (hover, focus) | ทำงานอัตโนมัติตามแบบ |
| ระยะเวลา | 0.3s - 1s (ปกติ) | 1s - หลายวินาที |
| การทำซ้ำ | ไม่ทำซ้ำ (แต่ละครั้งที่ event) | ทำซ้ำได้ (infinite) |
| Keyframes | ไม่ต้อง (2 state: from/to) | ต้องกำหนด @keyframes |
| ตัวอย่างใช้งาน | Button hover, color change, scale on hover | Loading spinner, bouncing ball, background scroll |
Best Practices & Tips
เพื่อให้ CSS ของคุณเป็นระเบียบ, มีประสิทธิภาพ, และดูแลรักษาได้ง่าย ให้ทำตามหลักการเหล่านี้:
1. Organize CSS Structure
จัดหมวดหมู่ CSS ตามลำดับเพื่อให้อ่านง่ายและหารือง่าย:
/* ===== RESET/NORMALIZE ===== */
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
/* ===== CSS VARIABLES ===== */
:root {
--primary-color: #3498db;
--spacing-unit: 8px;
--font-primary: Arial, sans-serif;
}
/* ===== BASE STYLES ===== */
body {
font-family: var(--font-primary);
}
/* ===== LAYOUT COMPONENTS ===== */
.container { }
/* ===== COMPONENTS ===== */
.button { }2. Use CSS Variables
ใช้ CSS Variables เพื่อให้ code อ่านง่าย, บำรุงรักษาง่าย, และสามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงได้ง่าย:
:root {
--primary-color: #3498db;
--spacing-unit: 8px;
--font-primary: Arial, sans-serif;
}
button {
background-color: var(--primary-color);
padding: calc(var(--spacing-unit) * 2);
}
/* เปลี่ยนค่าตาม media query */
@media (max-width: 768px) {
:root {
--spacing-unit: 4px;
}
}3. BEM Naming Convention
BEM (Block Element Modifier) ช่วยให้ชื่อ class ชัดเจน และป้องกันความขัดแย้ง:
/* Block */
.card { }
/* Element */
.card__header { }
.card__body { }
/* Modifier */
.card--featured { }
.card--disabled { }4. Mobile-First Approach
เขียน CSS สำหรับมือถือก่อน แล้วค่อยเพิ่มเติมสำหรับหน้าจอใหญ่:
/* Base: Mobile */
.container {
width: 100%;
}
/* Tablet */
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.container {
width: 750px;
}
}
/* Desktop */
@media (min-width: 1024px) {
.container {
width: 960px;
}
}5. Accessibility Best Practices
- Color Contrast - ทำให้ text อ่านได้ชัด (dark text on light background)
- Focus States - เพิ่ม :focus state สำหรับ keyboard navigation
- Font Size - ใช้ขนาด 16px ขึ้นไป เพื่อให้อ่านง่าย
- Line Height - ใช้ 1.5-1.8 เพื่อให้อ่านง่ายขึ้น
- Touch Targets - button/link ต้องขั้นต่ำ 44px
- ❌ Inline styles - ใช้ CSS file แทน
- ❌ pixel ทุกที่ - ใช้ relative units (rem, %)
- ❌ High specificity - เขียน selector ให้ simple
- ❌ !important abuse - ใช้ specificity ปกติแทน
- ❌ Ignoring mobile users - ทำ responsive design
✅ Summary - CSS Key Takeaways
- ✅ CSS Selectors - เข้าใจการเลือก elements ได้อย่างถูกต้อง
- ✅ Box Model - Margin, Border, Padding, Content ควบคุมพื้นที่
- ✅ Flexbox & Grid - สร้าง layout ที่ทันสมัยและเป็นระเบียบ
- ✅ Responsive Design - Mobile-first approach สำหรับทุกอุปกรณ์
- ✅ Colors & Fonts - เลือกสีและ font ที่สื่อถึงการออกแบบ
- ✅ Transitions & Animations - เพิ่มความมีชีวิตให้กับเว็บ
- ✅ Variables & Organization - ทำให้ CSS ค่อย, บำรุงรักษาง่าย
- ✅ Accessibility - ออกแบบให้ทุกคนสามารถใช้ได้
💡 Next Steps for Learning
- Practice CSS Selectors - สร้าง simple website เพื่อฝึกเลือก elements
- Master Flexbox/Grid - ทำ layout exercises บนอุปกรณ์ต่างๆ
- Learn a CSS Framework - ลอง Bootstrap, Tailwind, หรือ Material Design
- Build Responsive Websites - สร้างเว็บที่ทำงานบนทุกอุปกรณ์
- Learn SASS/SCSS - พัฒนา CSS skills ให้สูงขึ้น
- Understand Performance - เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับ CSS performance optimization
Tools & Resources
📚 Learning Resources
| Resource | ประเภท | Link | หมายเหตุ |
|---|---|---|---|
| MDN Web Docs | Documentation | https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS | 📌 ที่ดีที่สุด สำหรับ CSS reference |
| CSS Tricks | Blog/Guides | https://css-tricks.com | 📌 Tutorials และ tips เชิงลึก |
| Can I Use | Browser Support | https://caniuse.com | 📌 ตรวจ feature support ในเบราว์เซอร์ |
| CSS-Tricks Flexbox Guide | Guide | https://css-tricks.com/snippets/css/a-guide-to-flexbox/ | 📌 Flexbox ที่ดีที่สุด |
| CSS-Tricks Grid Guide | Guide | https://css-tricks.com/snippets/css/complete-guide-grid/ | 📌 Grid ที่ครอบคลุม |
🛠️ Useful Tools
| Tool | ใช้สำหรับ | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Chrome DevTools | Debug CSS, inspect elements, test responsive | Built-in browser tool (F12) |
| Prettier | Format CSS code | https://prettier.io |
| PostCSS | Transform CSS with plugins | https://postcss.org |
| SASS/SCSS | Write CSS dengan variables, nesting, mixins | https://sass-lang.com |
| Tailwind CSS | Utility-first CSS framework | https://tailwindcss.com |
🎨 Color & Design Tools
- Color Picker - https://colorpicker.com (เลือกสี)
- Coolors - https://coolors.co (Color palette generator)
- WebAIM Contrast Checker - https://webaim.org/resources/contrastchecker/ (ตรวจ color contrast)
- Google Fonts - https://fonts.google.com (Free fonts)
- Font Pairing - https://www.fontpair.co (ค้นหา font combinations)
📱 Responsive Testing
- Chrome DevTools Device Emulation (F12 → Toggle device toolbar)
- Responsively App - https://responsively.app (ทดสอบ responsive บนอุปกรณ์หลายตัว)
- BrowserStack - https://www.browserstack.com (ทดสอบบนเบราว์เซอร์จริง)